|
Liquid Cooling Basics.
As CPU speeds become faster and the desire to over-clock becomes stronger innovative methods to rid a computer system of destructive heat are being realized. One method that seems to be the next generation of system cooling is liquid cooling. Liquid cooling is the method of cooling a computer system using a liquid with limited use of fans. Whether you're intentions are in building a new computer or purchasing a new computer, liquid cooling is definitely worth your time looking into. What was once an exotic, sure-fire way to get looks of both astonishment and apprehension is now not only possible but practical and a highly efficient method of cooling your computer.
Liquid Cooling Components.
Before any liquid cooling concepts can be discussed an understanding must be had of key components that are involved in the liquid cooling process. Traditional cooling methods generally involve just two parts: heat sink and an accompanying fan. On the other hand, Liquid cooling has often been compared to the liquid cooling system in an automobile. This is a highly accurate comparison as the components involved in making each system work are very similar in function. No matter which liquid cooling system is chosen or how that particular system is implemented there are four main components: pump, water block, radiator, and a specific object to cool.
The pump is used to circulate the liquid throughout the system. This circulation is what makes liquid cooling possible making this liquid cooling component very important. A pump can get costly so careful consideration should be taken. Although many you will find many varieties of pumps you should be aware 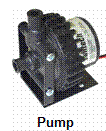 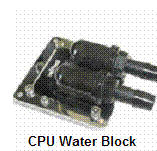  of two types: saturated or dry. of two types: saturated or dry.
A saturated pump must be kept in a tank of the liquid you choose to cool your system. This is because water is absorbed into the pump. A dry pump however is usually the one you want as this system is more self contained.
The water block is the component that does the actual transfer of heat from the computer part to the liquid. At the beginning stages of liquid cooling only one part , the CPU, was being cooled by liquid so only one water block was needed. In the present however, computers are being equipped with liquid cooling for the entire system creating a need for multiple and improved water blocks. It should be mentioned that water blocks can be bought that cool more than one component at a time.
In a typical, customized, computer system the radiator is usually in the form of a heatsink. A heatsink is a metal component with comb-like sections often used to cool parts in a high-tech customized system. A fan is usually used in conjunction with a heatsink in order to dissipate the heat more quickly optimizing the set-up. Some high-tech explorers have demonstrated the possibility to use an actual car radiator. This method, though intriguing, is not practical for most computer systems. Many variations of heat-sinks exist so finding the right one is just a matter of research.
Now this might seem trivial to point out but a specific object needs to be cooled. Liquid cooling is not similar to traditional heat sink and fan methods which enable a simple set-up which will cool the entire computer. Sure, the entire computer can be cooled by liquid cooling alone but each individual part needing cooling must be addressed independently.
Those are the main ingredients to the liquid cooling recipe. Still, in order to complete the system several other parts are also either very helpful or necessary. A reservoir is one of these parts. This is used to hold the liquid and bleed the system. Bleeding the system is the process of ridding the tubing of air bubbles or possible chemical formations. Tubing is another necessary part to a liquid cooling system. Once again, you have many options available and only some diligent research will be able to tell you the best option for you. A part that is not needed in the fundamental operation of a liquid cooling system though is highly recommended is a flow indicator. A flow indicator is a device that is used to quickly check if liquid is circulating properly. A flow indicator fits right in-line with the tubing and actually does not look out of place with the tubing. The last part that should be mentioned is the liquid itself. Water is not advisable. The minerals in water will build up algae and other bacteria will form in no time. Therefore distilled water should be used. With distilled water alone a problem still exists. The risk of oxidation (rust) is very high when water is cycled through different metal components frequently so an anticorrosion additive should be used. This is very inexpensive and can be purchased at many computer outlets and usually comes with a liquid cooling kit.
Advantages of Liquid Cooling.
There are several key advantages to selecting a liquid cooling method to stop the spread of possibly detrimental and costly heat created by the hard-working parts of a computer. Liquid cooling does not necessarily require the fans required for cooling that a traditional system would. This absence of fans allows this cooling approach to be much quieter. The next advantage is really what matters to most of us who wish to have a liquid cooling system installed. This is the performance advantage. Performance can be greatly improved over traditional methods of computer system cooling. Ten percent of fatal computer issues are cooling related. This percentage can be drastically reduced by using the liqu  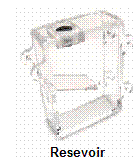 id cooling approach. id cooling approach.
Disadvantages of Liquid Cooling.
Although deciding to use liquid cooling as a means to reduce internal temperature of your computer has many advantages, there are some disadvantages of liquid cooling that should be addressed and taken into consideration when selecting the best liquid cooling system for you. In some instances liquid cooling is not the optimum cooling method. In these occurrences other methods of heat absorption should be implemented that specifically address the needs of that particular system. These other methods which could serve to be more rewarding will be briefly explained in the next section. The most glaring disadvantage to liquid cooling is the technical level of installation. Liquid cooling should not be attempted unless the installer knows the install process exactly and what to do should an issue arise. Expensive damage can easily be done to internal components if the system is not installed correctly. During the installation the risk is especially high that computer system components will be harmed or the individual doing the installation will be harmed. Nevertheless, if approached with caution liquid cooling can be implemented safely and without any electrical casualties.
Liquid Cooling Options.
As stated above a monopoly over the liquid cooling technology does not exist creating many options available to the consumer. Whole kits can be purchased for just a couple hundred dollars. This amount will only go down. Another option that some have shown interest in is a, pre-built, liquid cooled case. These are usually between $500 and $2,000 however can save a lot of time and money in the long run. Sometimes liquid cooling is not the best bet. High-tech heatsinks and fans can be quieter than factory fans and dissipate heat effectively for most users. A quick sit-down thinking out available space and technical prowess will guide you toward the perfect cooling option.
With the need for higher performance comes the need for better heat reduction. Liquid cooling is proving itself to be the next generation of cooling. Top of the line Mac G5 computers as well as several other companies high-end computer systems are being equipped with liquid cooling. This just goes to show that technology has no bounds. Even when combining water and electricity.
 Back To Hardware Guides Back To Hardware Guides
Popular Articles:
How To Build A PC | Different Types of Keyboards | Help with Hard Drive Installation | Computer Networking Basics | Introduction of Motherboard Functions | Computer CPU Processor Speed | Upgrade from Windows 95 to Windows 98 | Computer Monitor Troubleshoot | Partition Hard Drive | Installing New CPU Processor | Types of Network Cables |